Epithalon (Epitalon) 50 mg
$130.00
In stock
| Quantity | Quantity | Price per Vial |
|---|---|---|
| Quantity Based Discount | 2 - 4 | 5% $123.50 |
| Quantity Based Discount | 5 - 9 | 10% $117.00 |
| Quantity Based Discount | 10 - 19 | 15% $110.50 |
| Quantity Based Discount | 20 + | 25% $97.50 |
What is Epithalon (Epitalon)?
Epithalon (also known as Epitalon) is a synthetic tetrapeptide made up of four amino acids: alanine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid, and glycine (Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly). Developed for scientific research, Epithalon is studied primarily for its potential impact on telomerase activation, cellular longevity, immune modulation, and circadian rhythm regulation.
This research peptide is valued for its stability in lyophilized form, excellent solubility in sterile water, and high purity, making it suitable for controlled laboratory settings. Its structure allows for easy handling and accurate dosing in various in vitro and in vivo research protocols.
| Note: Evolve Peptides sells Epitalon for research use only. It is not approved for human consumption, veterinary use, or therapeutic applications. |
Epithalon Mechanism of Action (Based on Research)
Epithalon (Epitalon) is a synthetic tetrapeptide (Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly) investigated for its potential to modulate aging-related biological processes. Its mechanisms of action have been primarily explored in non-clinical studies involving animal models, cell cultures, and limited human cohorts.
The following pathways are among the most studied.
Telomerase Activation and Telomere Maintenance
Epithalon has been shown to activate telomerase, an enzyme responsible for extending telomeres.
Telomeres are the protective caps at the ends of chromosomes. They are nucleotide sequences that protect chromosomal ends from degradation and fusion during replication. Telomere shortening is a key hallmark of cellular senescence (a state where cells permanently stop dividing but don’t die).
By maintaining telomere length, Epithalon may delay cellular senescence and support genomic stability in aging cells. In vitro studies using human somatic cell cultures demonstrated that Epithalon significantly increased telomerase expression and activity, thereby preserving telomere length and delaying replicative senescence [1].
Support of Cellular Longevity and Mitochondrial Function
In animal studies, prolonged administration of Epithalon was associated with increased lifespan and improved markers of physiological function in aging rodents. This effect is believed to be linked to reduced oxidative stress and improved mitochondrial efficiency.
In rodent models, long-term administration of Epithalon was associated with increased lifespan, reduced tumor incidence, and improved markers of physical function in aged animals. The proposed mechanism includes modulation of oxidative stress and mitochondrial biogenesis. [2].
By influencing gene expression involved in antioxidant defense and apoptosis regulation, Epithalon may enhance cellular resistance to oxidative damage, a critical factor in the aging process. Evidence also suggests improved function of mitochondrial enzymes such as cytochrome c oxidase, which play roles in energy metabolism and redox balance.
Immune Modulation and Thymic Activity
Research suggests Epithalon may influence thymic peptide production and immune homeostasis in aged organisms.
In animal studies on aging, Epithalon has demonstrated immunomodulatory properties. It appears to restore or enhance T-lymphocyte function and normalize cytokine profiles, possibly by acting on the thymus gland—an organ that undergoes involution with age.
In these studies, Epithalon administration in elderly or immunosuppressed animals leads to increased production of thymic peptides and improved immunological parameters, including CD4/CD8 ratios and natural killer (NK) cell activity [3].
Regulation of Circadian Rhythms and Pineal Function
Epithalon was originally derived from epithalamin, a peptide extract of the pineal gland. Subsequent studies have shown that it can influence melatonin secretion, a key regulator of circadian rhythms and sleep-wake cycles.
In aging non-human primates, Epithalon helped normalize the circadian release of melatonin by restoring pineal gland function, which typically declines with age. These regulatory effects may underlie observed improvements in sleep-wake patterns and neuroendocrine homeostasis in aged subjects [3].
Epithalon Research Applications (Benefits)
Epithalon is gaining attention for its potential anti-aging benefits. Research highlights its role in extending cellular lifespan, enhancing immune function, regulating melatonin secretion, and protecting genomic stability.
These diverse applications position Epithalon as a promising compound in age-related health and regenerative medicine studies.
1. Telomere Support & Cellular Longevity
Epithalon has been demonstrated to significantly activate telomerase and elongate telomeres in human somatic cells cultured in vitro.
In a seminal study, researchers added Epithalon to human fetal fibroblasts that lacked detectable telomerase activity. The result: telomerase catalytic subunit expression was reactivated, enzyme activity increased, and telomere lengthening occurred, effectively extending the cells’ proliferative capacity from ~34 to over 44 passages [1].
This bypass of the traditional Hayflick limit suggests a profound impact on cellular replicative lifespan. In vivo, rodent studies indicate that Epithalon reduces chromosomal aberrations in aging mice, which is a marker of genomic stability [3].
Circadian Rhythm & Melatonin Regulation
Epithalon’s origins from epithalamin link it directly to melatonin regulation and circadian rhythm dynamics. In aged non-human primates and elderly humans, studies show that Epithalon or epithalamin administration restored nocturnal melatonin secretion, suggesting a rejuvenation of the pineal endocrine function [4].
In controlled lighting studies involving rodents subjected to constant illumination (a stressor that disrupts circadian patterns), intermittent Epithalon treatment normalized melatonin and cortisol rhythms, partially preserving typical day–night physiological cycles [2][4][5].
Additionally, human thymic–pineal studies documented improved sleep–wake hormone regulation following peptide administration. For researchers, these findings highlight Epithalon as an intriguing tool for exploring pineal-pineal axis regulation, chronobiology, and age-associated endocrine decline.
Immune System Modulation & Thymic Support
Several animal studies reveal that Epithalon may influence immune organ restoration, particularly the thymus gland, which naturally involutes with age.
In neonatal hypophysectomized or aged chickens and mice, peptide treatment promoted thymic tissue recovery, increased lymphocyte proliferation, and elevated interferon-gamma production from T-cells [4].
In aged CBA mice, in vitro treatment with Epithalon (and its pineal precursor epithalamin) enhanced the thymus microenvironment by increasing stromal precursor fibroblasts and thymic serum factor. It also raised CD4⁺ T-cell proportions in the bone marrow and modulated splenic CD8⁺ cells, indicating rejuvenation toward a younger immune phenotype [5].
In aged CBA mice, in vitro treatment with Epithalon (and its pineal precursor epithalamin) enhanced the thymus microenvironment by increasing stromal precursor fibroblasts and thymic serum factor. It also raised CD4⁺ T-cell proportions in the bone marrow and modulated splenic CD8⁺ cells, indicating rejuvenation toward a younger immune phenotype.
Oxidative Stress Reduction & Antioxidant Effects
Research indicates that Epithalon may play a role in mitigating oxidative damage—a key mechanism in cellular aging.
In aged rat models, treatment increased activity of antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase, and glutathione-S-transferase, improving overall oxidative defense.
Cell culture studies further reveal lowered lipid peroxidation and markers of reactive oxygen species following Epithalon exposure—indicating a protective effect on cellular membranes and biomolecules . These antioxidant effects, combined with telomere stabilization, support a multi-layered model of how Epithalon might delay molecular aging [3].
Oncostatic & Genomic Integrity Effects
Epithalon’s potential oncostatic (anti-cancer) properties are supported by animal studies showing reductions in spontaneous tumor incidence and metastasis, especially among aged rodents [4].
These outcomes reflect the peptide’s broader roles in DNA stabilization and immune surveillance, alongside telomere maintenance.
Mechanistic work also highlights Epithalon’s ability to inhibit MMP-9, a matrix metalloprotease involved in tumor invasiveness and metastasis. In cultured fibroblasts, this inhibition suggests regulatory control over cell migration and extracellular matrix remodeling [3].
Epithalon Peptide Characteristics
- Molecular Formula: C₁₄H₂₂N₄O₉
- CAS Number: 307297‑39‑8
- Synonyms: Epitalon, Epithalon, Epithalone, AEDG
- Molar Mass: 390.35 g/mol (≈ 390.34 Da)
- Appearance: White to off-white lyophilized powder
- Solubility:
- ≥50 mg/mL in water (≈128 mM)
- Soluble in DMSO up to ~250 mg/mL (≈496 mM)
- Storage Recommendations
- Dry, lyophilized form: Store at ≤ –20 °C (preferably –80 °C for long-term)
- In water/PBS/Saline – store at –80 °C up to 6 months, or –20 °C up to 1 month
Epithalon vs FOXO4-DRI vs Thymalin Comparison
| Feature | Epithalon | FOXO4-DRI | Thymalin |
| Type | Synthetic tetrapeptide (Ala‑Glu‑Asp‑Gly) | Cell-penetrating senolytic peptide (D‑Retro‑Inverso peptide targeting FOXO4–p53 interaction) | Polypeptide drug derived from calf thymus; mixture of small peptides |
| Targets | Telomerase activity, pineal and thymic function | Senescent cells via FOXO4–p53 pathway | Thymus gland, T-cell maturation |
| Mechanism Complexity | Moderate (telomerase + neuroendocrine + immune) | High (precision senolytic targeting) (Disrupts FOXO4–p53 in senescent cells) | Simple/moderate (immune regeneration) |
| Research Stage | Preclinical and limited human trials | Preclinical (cell culture, mice); In vitro and animal models of senescence & aging | Preclinical and historical clinical use in immune deficiency and infections |
| Longevity Focus (Research) | Delayed aging, extended lifespan in rodents | Senescent cell clearance; improved function in aged mice | May restore circadian-linked immune rhythms; less direct lifespan study |
| Immune Modulation | Yes (restores pineal–thymic axis); Thymic and pineal axis balance |
Indirect via clearing SASP-producing cells | Direct enhancement of T‑cells, NK activity, and immune recovery |
| Circadian Support | Indirect; Affects melatonin rhythm via pineal peptide action | Not reported | Mild influence; May modulate circadian immune rhythms |
| Dosing Frequency (Studies) | Cycled (e.g., 10-day protocols) | Experimental; Short courses (e.g. 3 doses) in mice | Daily or cyclic, varies by study |
| Approval Status | Research use only | Research use only | Research use only (past clinical use in some countries) |
| Disclaimer | Not for human consumption | Not for human consumption | Not for human consumption |
Safety and Side Effects in Studies
Research on Epithalon (Epitalon) has primarily been conducted in animal models and in vitro, with limited early human observations. Within these controlled research settings, no significant adverse effects have been reported at studied dosages.
In one 6.5-month study on C3H/He mice receiving 0.1 μg Epitalon daily, no toxic effects were observed, even as tumor incidence and metastases decreased [6].
In another, a lifespan trial in Swiss-derived SHR mice (1 μg/mouse per month) reported no changes in food intake or body weight, while chromosomal aberrations decreased and maximum lifespan increased [7].
Extended dosing (100 μg/day for six months) in rodents also showed no reported toxicity or organ abnormalities.
Anecdotal human data and limited early-stage trials have also not documented systemic adverse effects, though subcutaneous/intramuscular peptides, in general, may cause mild local irritation.
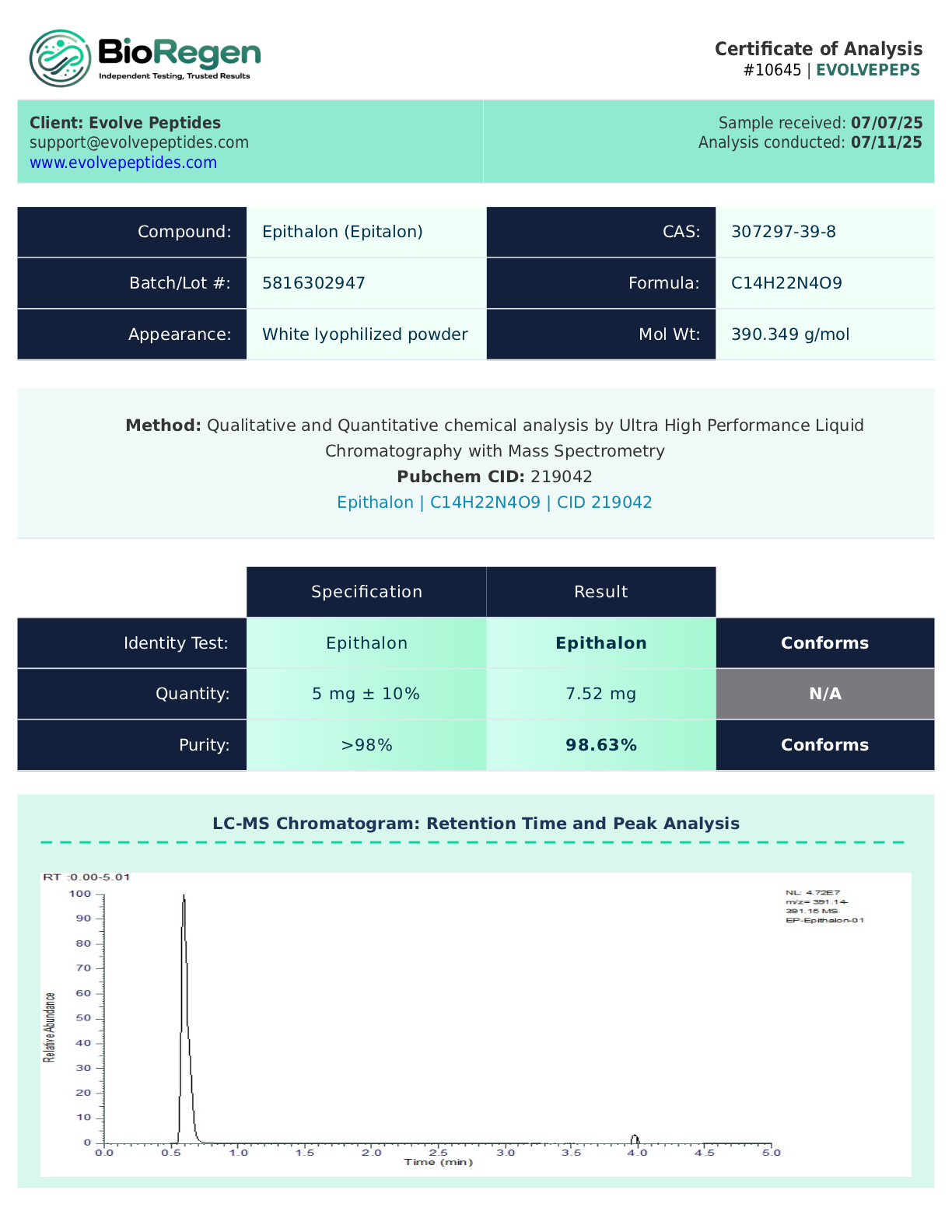
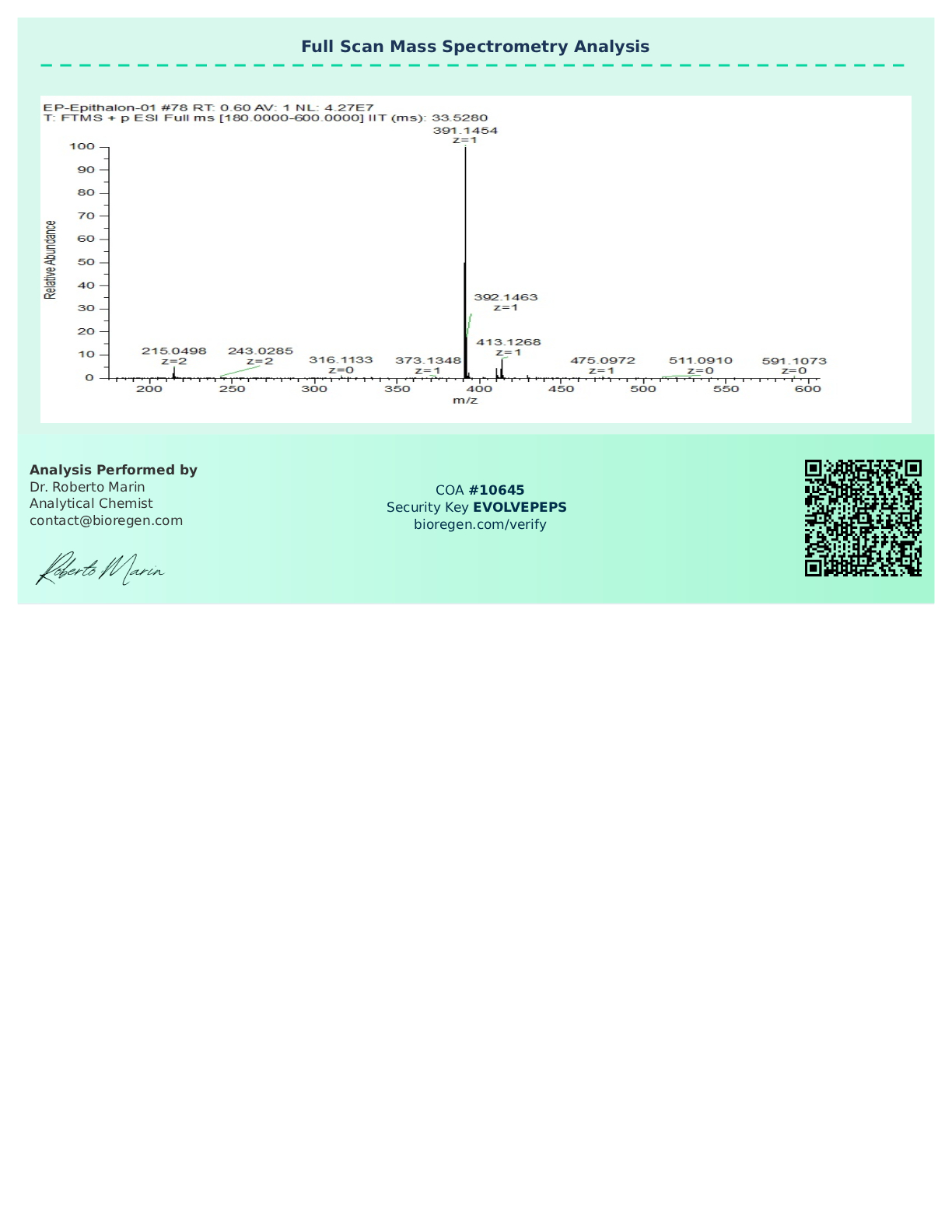
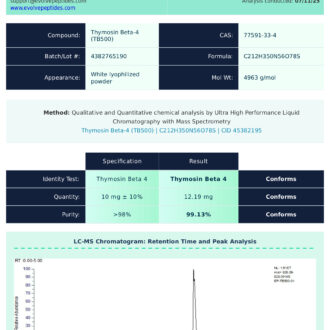
Certificate of Analysis (COA)
Every batch of Epithalon available at Evolve Peptides is verified through independent third-party laboratory testing. This ensures that each vial meets rigorous specifications for:
- Purity (≥99%)
- Identity verification
- Sterility and microbial testing
- Endotoxin levels (where applicable)
Our COAs are batch-specific and can be provided upon request. For transparency and quality assurance, we make sample COAs available for review on select product pages.
Legal Disclaimer
This product is intended strictly for laboratory research purposes and is not approved for human or veterinary use. It is supplied exclusively to qualified professionals, institutions, or laboratories conducting in vitro or preclinical studies.
Epithalon sold by Evolve Peptides is not intended for ingestion, injection, or topical application in humans or animals. Any use outside of a controlled laboratory environment is expressly prohibited.
This product is not for resale, and may not be used in diagnostic, therapeutic, or clinical applications of any kind. Buyers are responsible for ensuring compliance with all applicable local, state, and federal regulations regarding the use of research chemicals.
Scientific References
- Khavinson, V. K., Bondarev, I. E., & Butyugov, A. A. (2003).
Epithalon peptide induces telomerase activity and telomere elongation in human somatic cells.
Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 135(6), 590–592.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1023/A:1025493705728 - The International Peptide Society. (2018).
Epithalon monograph.
Retrieved July 2025, from
https://peptidesociety.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/Epithalon-Monograph-Final.pdf - Araj, S. K., Brzezik, J., Mądra-Gackowska, K., & Szeleszczuk, Ł. (2025).
Overview of Epitalon—Highly Bioactive Pineal Tetrapeptide with Promising Properties.
International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2691.
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/26/6/2691 - ChemicalBook. (2021, March 17).
Biological effects of Epitalon.
ChemicalBook. Retrieved July 10, 2025, from
https://www.chemicalbook.com/article/biological-effects-of-epitalon.htm - Korenevsky, A. V., Milyutina, Y. P., Bukalyov, A. V., Baranova, Y. P., Vinogradova, I. A., & Arutjunyan, A. V. (2014).
The protective effect of melatonin and epithalon on hypothalamic regulation of the reproductive function in female rats in a model of its premature aging and on the estrous cycles of aging animals in different lighting conditions.
Advances in Gerontology, 4(4), 67–77.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1134/S2079057014010044 - Labunets, I. F., Butenko, G. M., & Khavinson, V. K. (2004).
Effects of bioactive factors of the pineal gland on thymus function and cell composition of the bone marrow and spleen in mice of different age.
Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 137(5), 510–512.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11943447/ - Kossoy, G., Chepurnov, S. A., Anisimov, V. N., & Khavinson, V. K. (2006).
Effect of the synthetic pineal peptide epitalon on spontaneous carcinogenesis in female C3H/He mice.
Experimental Oncology, 28(1), 30–35.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16634527/ - Anisimov, V. N., Khavinson, V. K., Popovich, I. G., Zabezhinski, M. A., Alimova, I. N., Rosenfeld, S. V., Zavarzina, N. Y., Semenchenko, A. V., & Yashin, A. I. (2003).
Effect of Epitalon on biomarkers of aging, life span and spontaneous tumor incidence in female Swiss-derived SHR mice.
Biogerontology, 4(4), 193–202.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14501183/
Contents: 50 mg lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder provided in a 3 ml vial, sealed and sterile. Purity exceeds 99%, guaranteed.
Notes: Requires reconstitution with bacteriostatic water. (Sold Here: BAC Water.)
Chemical Formula: C14H22N4O9
PubChem CID: 219042
CAS Number: 307297-39-8
Molecular Weight: 390.35 g/mol
Storage: Store at ≤8°C, sealed, away from heat, light, and moisture. The colder the better.
Purity: >99%
Orders placed before 1 PM EST ship same day.
We use USPS for most of our deliveries. You can expect your parcel within 2-5 business days from when it leaves our warehouse.
Why Choose Us?
Potency & Purity Guaranteed
Our peptides are custom-manufactured to exact specifications. Strictly no compromises.
Rigorously Third-Party Tested
Every product page includes independent lab test results for every peptide we sell.
Dedicated End-to-End Support
We're here for you every step of the way. Our goal is your success in research.
100% Satisfaction Guaranteed
If you are not 100% satisfied with our research peptides, we'll refund everything you paid.